Objectives
At the end of the lesson, you should be able to:
- describe the different types of scientific investigations: and
- identify different scientific tools used in scientific investigations.
Scientific Investigation
- A scientific investigation is a scientist’s efficient approach to research and answers a problem implementing the scientific method.
- Scientists use multiple research methods to study the natural world. There are three types of scientific investigations:
- descriptive investigation;
- comparative investigation; and
- experimental investigation.
1. Descriptive Investigation
- It primarily observes, describes, and measures different parts of the system.
- It is used when studying an object or situation for the first time.
- Observations derived from this type can be qualitative or quantitative and represented as diagrams.
Example
The descriptive investigation may be used to identify and describe the temperature of ice, the shape of ice (whether it’s tube, cube, or block), or how fast does an ice melt on a summer day.
2. Comparative Investigation
- It shows a relationship between two or more seemingly related subjects or conditions.
- It involves collecting data on different subjects or different conditions and evaluating them based on similarities and differences.
Example
You want to know “Which will melt faster, ice with salt or without salt?”
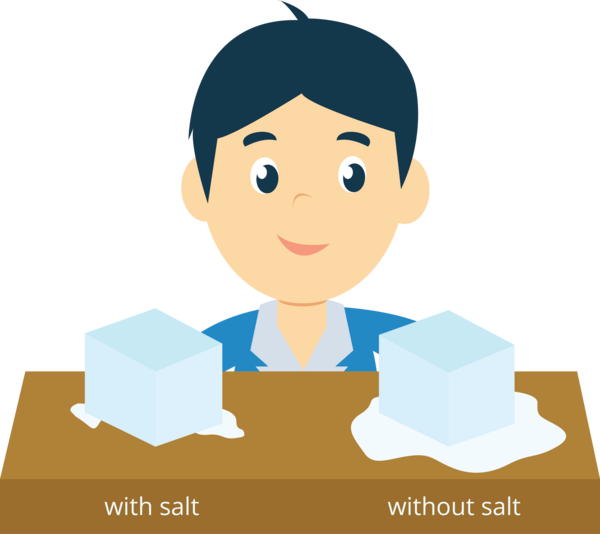

You can easily set up an experiment to measure the time in which the ice with salt and the ice without salt will melt.
3. Experimental Investigation
- It is used when scientists want to learn more about a subject
- It is also used to determine the effects of changing a certain variable
- Variables are manipulated, controlled, and measured using the scientific method
Example
You want to know if the length of the string affects the time it takes a pendulum to complete a full swing. You can design your experimental investigation based on the scientific method.
1. Observation: A shorter pendulum seems to swing faster than a long pendulum. You measure the length of the string of both pendulums. The shorter pendulum is at 15.0 cm while the longer one is at 25.0 cm.
1. Statement of the problem: How does the length of the string affect the time it takes for a pendulum to complete a full swing?
1. Collect preliminary data: The time it takes for a pendulum to complete a full swing is called a period. Mechanical energy is conserved in a pendulum motion.
1. Hypothesis: As the length of the string increases, the period also increases.
1. Experiment: The length of the string can be varied and its effect can be checked by measuring the period. The length of the string is the independent variable, while the period is the dependent variable.
1. Collect and analyze data: Record observations and present them in a table. A line graph can be constructed to show how the period increases with the length of the string.
1. Conclusion: The length of the string is directly proportional to the period.
Key Points
- A scientific investigation is a scientist’s efficient approach to research and answers a problem implementing the scientific method.
- A descriptive investigation is used when you are studying an object or situation for the first time.
- A comparative investigation shows a relationship between two or more seemingly related subjects or conditions.
- An experimental investigation is used when scientists want to learn more about a subject.
Comments
Post a Comment